Laser marking is widely used on plastic parts today.
But during daily communication with customers, one question comes up again and again.
If laser marking is already common on plastic, why do some parts turn yellow, brown, or even look slightly burned after marking?
This issue is especially serious for medical devices and electronic components.
In these industries, even small color changes can cause parts to fail inspection and lead to rework or scrap.
In this article, HANTENCNC shares what we see in real marking tests, explains why plastic turns yellow after laser marking, and shows which methods only reduce the problem and which ones can truly solve it.
1. The Real Reason: Local Heat Damage, Not Poor Plastic Quality
Laser marking always creates heat.
At the same time, most plastics are very sensitive to temperature.
When laser energy is focused on the surface and heat cannot spread fast enough, several reactions may happen.
The polymer structure can start to break down.
The surface may react with oxygen.
Some additives inside the plastic may change color.
This usually does not burn through the plastic.
Instead, yellow or brown marks appear around the marking area.
In our own sample tests, even plastics with good surface quality will turn yellow if the heat input is too high.
This is not unusual. It is a normal reaction of plastic to excessive heat.

2. Why Fiber Laser Marking Causes Yellowing More Often
Fiber laser marking machines work at a wavelength of 1064 nm.
This wavelength is mainly designed for metal marking.When a fiber laser is used on plastic, several problems appear.Plastic does not absorb 1064 nm laser energy very well.
Most of the laser energy turns into heat instead of clean marking.Heat stays on the surface and causes burning or discoloration.During customer tests, we often see the same result.
ABS or PC housings marked with a 20W to 30W fiber laser still turn yellow, even after power is reduced.In most cases, this means the issue is not the parameter settings.
It means the laser type does not match the material.
3. Which Plastics Turn Yellow Most Easily?
Based on our application experience, some plastics are more sensitive to heat than others.
| Plastic Type | Risk of Yellowing |
| ABS | High |
| PVC | High |
| PC (Polycarbonate) | High |
| PE / PP | Medium |
| Medical-grade plastics | Very high |
4. Why UV Laser Marking Can Prevent Yellowing
UV laser marking machines work at 355 nm, which is a much shorter wavelength.More importantly, UV lasers interact with plastic in a different way.
The marking process is mainly based on a photochemical reaction, not heat.
The heat affected area is very small.The plastic surface does not melt or burn easily.
In side-by-side tests on the same ABS or PC material, UV laser marking produces clean edges and stable color, with almost no visible heat marks.
Because of this, UV laser marking is often called cold laser marking.
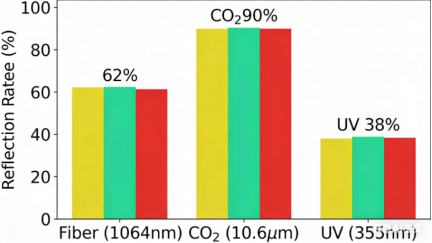
5. Fiber Laser vs UV Laser for Plastic Marking
| Item | Fiber Laser | UV Laser |
| Wavelength | 1064 nm | 355 nm |
| Heat impact | High | Very low |
| Yellowing on plastic | Common | Rare |
| Edge quality | Easy to melt | Clean and sharp |
| Suitability for plastic | Not recommended | Very suitable |
6. Can Parameter Adjustment Fix Yellowing?
This is one of the most common questions we receive.
In some cases, reducing power, increasing marking speed, or lowering repeat passes can reduce yellowing.
However, in our tests, even when non-UV laser machines are pushed to their limits, the result is usually the same.
Marking contrast becomes weaker.
Yellowing is reduced, but not completely removed.
This shows that the core issue is not the parameters.
It is the laser technology itself.

7. Applications Where UV Laser Marking Is Required
In the following applications, even slight yellowing is not acceptable.
Medical devices and disposable medical products
Electronic connectors and precision housings
Cosmetic and premium packaging
Pharmaceutical packaging and traceability marks
PCB boards and micro components
8. How to Know If Your Plastic Should Use UV Laser Marking
Based on recent sample tests and customer projects, we suggest checking the following points before choosing a marking solution.
Plastic type and formulation
Visual quality requirements
Industry compliance standards
Long-term production stability
If two or more of these points are critical, using a fiber laser often leads to higher rework and adjustment costs.
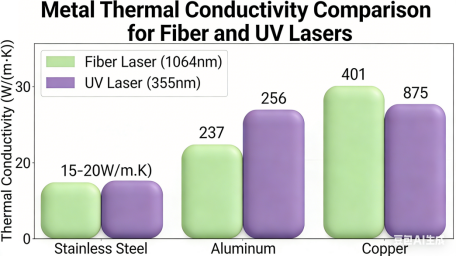
9. Yellowing Means the Technology Is Not a Match
When plastic turns yellow after laser marking, it is usually not a material defect and not an operator mistake.
It is a mismatch between laser technology and the material.
Different lasers are designed for different tasks.
Fiber lasers are ideal for metal marking.
UV lasers are better for plastic and fine marking.
In real production, choosing the right laser type is often more effective and more economical than adjusting parameters again and again.
Need Help With Plastic Laser Marking?
If you are not sure which laser is suitable for your plastic parts, we usually recommend testing samples first before choosing a machine.
Real marking results give clearer answers than specifications alone.
In these industries, UV laser marking is no longer a high-end option.
It is simply a safer and more stable choice.